A Strange Geological Mechanism Explains How The Solar Systems Icy Moons Formed
A Strange Geological Mechanism Explains How The Solar Systems Icy Moons Formed


Scientists found that the melting of the ice crust from below leads to the boiling of the water oceans inside it.
Moons such as Saturn’s Enceladus are among the most promising places in our solar system to search for life outside Earth, as they are believed to contain oceans of liquid water beneath their frozen icy crust.
The new study seeks to understand the geological processes that shape the surface of these mysterious worlds.
How does geology work on icy moons?
The geology of these moons works differently than on Earth. While the geology of our planet depends on the movement of rocks and lava, the geology of icy moons depends on the interactions of water and ice. These moons are heated by gravitational forces from the parent planets orbiting them, causing alternating cycles of ice melting and freezing.
As the ice layers thicken, they put pressure on the surface crust, causing prominent cracks such as those known as “tiger stripes” on Enceladus’ surface. But when the ice begins to melt from below, the sharp drop in pressure can cause a unique phenomenon: the oceans hidden beneath the surface to boil.
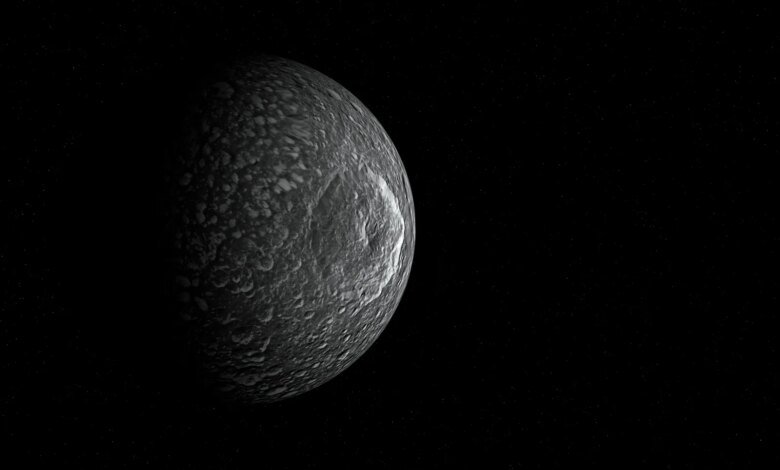
This boiling occurs because the transformation of ice into liquid water leads to a significant drop in pressure, especially in small moons such as Mimas Enceladus of Saturn and Miranda of Uranus, where the pressure can reach the point where ice, water and steam exist simultaneously. This phenomenon may provide a convincing explanation for the strange geological formations that scientists observed in the images taken by the Voyager 2 probe of the surface of the moon Miranda, including complex networks of hills and slopes.
The size of the Moon plays a crucial role in determining the nature of these geological processes. In small moons, boiling can occur in the inner oceans without the icy surface cracking, while in larger moons such as Uranus’s Titania, the icy crust cracks and cracks before it reaches the boiling stage.
This study reveals surprising dynamics of icy ocean worlds, expanding our understanding of the processes that can shape the environments of these distant bodies and influence their habitability.
Source: Eurekalert
Disclaimer: This news article has been republished exactly as it appeared on its original source, without any modification. We do not take any responsibility for its content, which remains solely the responsibility of the original publisher.
Author:
Published on:2025-11-26 08:38:00
Source: arabic.rt.com
UAETodayNews delivers the latest news and updates from the UAE, Arab world, and beyond. Covering politics, business, sports, technology, and culture with trusted reporting.
Disclaimer: This news article has been republished exactly as it appeared on its original source, without any modification. We do not take any responsibility for its content, which remains solely the responsibility of the original publisher.
Author: uaetodaynews
Published on: 2025-11-26 10:15:00
Source: uaetodaynews.com